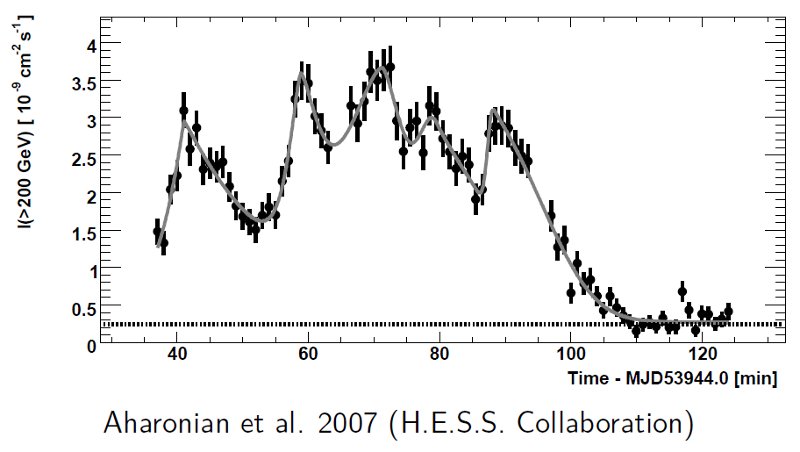
Rapid variability of PKS 2155-304 - observed by H.E.S.S. observatory. At least five outburst were observed in about 1.5 hour.
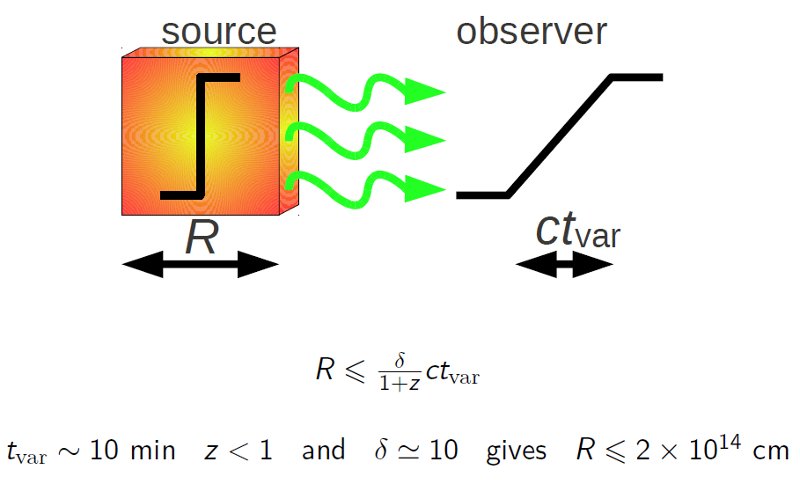
Variability time scale constrains the source size. A rapid change
of the source emission ![]() is observed for time tvar in the observer's frame. This parameter
gives an upper limit for the source size (R≤tvar/c). In addition,
for relativistically moving sources (Doppler factor δ > 1) at cosmological
distances (redshift z>0) it is necessary to apply adequate transformation
of time. The variability time scale of PKS 2155-304 of about 5 minutes gives an
upper limit for the source size of about 1014 cm.
is observed for time tvar in the observer's frame. This parameter
gives an upper limit for the source size (R≤tvar/c). In addition,
for relativistically moving sources (Doppler factor δ > 1) at cosmological
distances (redshift z>0) it is necessary to apply adequate transformation
of time. The variability time scale of PKS 2155-304 of about 5 minutes gives an
upper limit for the source size of about 1014 cm.
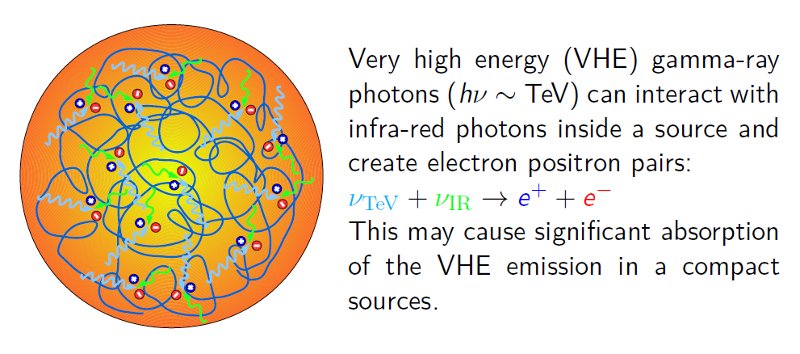
Pair absorption. A small source must be relatively dense to explain the observed level of the emission. Therefore the absorption of the VHE radiation can be significant inside such source. An alternate approach assumes a low density source that travels with hig relativistic velocity (δ >> 50).
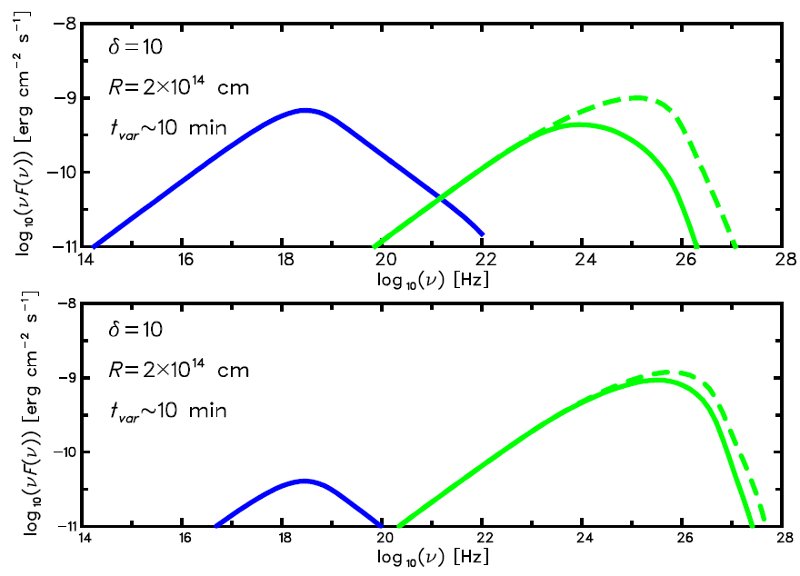
An example of the pair absorption. The figure shows theoretical synchrotron and inverse-Compton spectra of a compact source. In the upper panel the level of the synchrotron emission is comparable with the inverse-Compton spectrum and the pair absorption is significant (dashed line shows unabsorbed spectrum). The lower panel shows the case where synchrotron emission is significantly lower than the inverse-Compton radiation. In such a case the pair absorption is almost negligible.
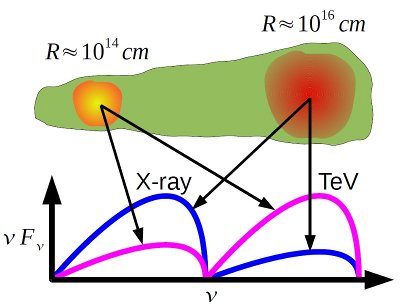
The main assumption of the model. The emission in the X-ray range is dominated by a blob (c1) two orders of magnitude bigger than blobs (c2..6) that are producing the rapid TeV variability. This allows to use moderate value of the Doppler factor of blobs (D=20..30) to explain this rapid variability.
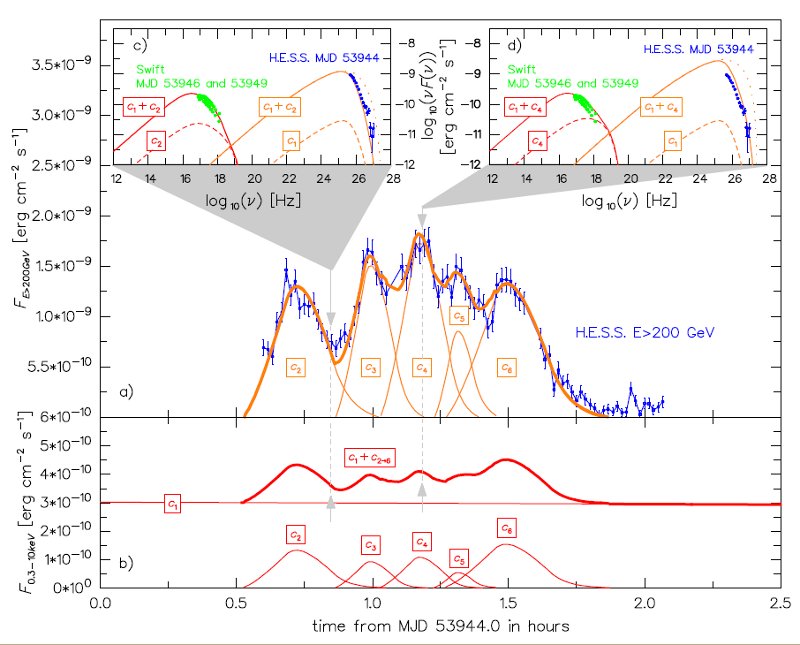
Results of the modeling The main frame shows the observed gamma-ray light curve and the predicted gamma-ray and X-ray light curves. The sub-panels show spectra at two different time moments. The activity is well reproduced by emission of six (c1...6) independent jet's components (for more details see Katarzynski et al. MNRAS 2008).
|
Copyright © K. Katarzynski 2022. All rights reserved. back to main page |